 PeriodicTable
PeriodicTable
Franklin D. Roosevelt’s Periodic Table World War II
World War II
slovakiaOperation Overlord"Final Solution"Gas ChamberSchutzstaffelNazi-Soviet Non-Aggression PactNuremberg TrialsFour Freedoms"Germany First"United Service OrganizationsUnited NationsHolocaust
- Major Allied Powers
- Major Axis Powers
- Major Allied Powers
- Home Front
- Major Axis Powers
- Major Allied Powers
- Battles and Events
- Home Front
- Major Axis Powers
Rights: To the best of our knowledge, these images are in the public domain and can be used without further permission.
United States of America
The United States of America joined WWII on December 8, 1941 after the attack on Pearl Harbor.
Germany
Germany began WWII with the invasion of Poland on September 1, 1939.

United Kingdom
The United Kingdom joined WWII on September 3, 1939 after the invasion of Poland.

Soviet Union
The Soviet Union joined WWII on June 22, 1941 after the German invasion of the Soviet Union.

Rationing
During WWII, a rationing system was implemented in the United States. Each person in a household could receive a ration book with ration stamps.

"Rosie the Riveter"
"Rosie the Riveter" was a cultural icon in the U.S. that represented all of the women who entered the work force for the first time furing WWII, many into manufacturing jobs.

Propaganda
Progaganda movies and posters during WWII helped to mobilize the nation by linking the military front and the home front. Through this effort Americans were called upon to boost production at work and at home.

The Draft
The Draft, which was first passed in 1940, sought to bolster the numbers of the U.S. military.

Isolationists
At the beginning of the war, many Americans were isolationists. They did not want the U.S. to become entangled with foreign conflicts.

Italy
Italy entered WWII on June 10, 1940.

China
The Republic of China joined WWII officially on December 9, 1941.

Poland
Poland joined WWII on September 1, 1939 after it was invaded by Germany.

Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain, fought during 1940, was a battle between the Germans and the British for air superiority.

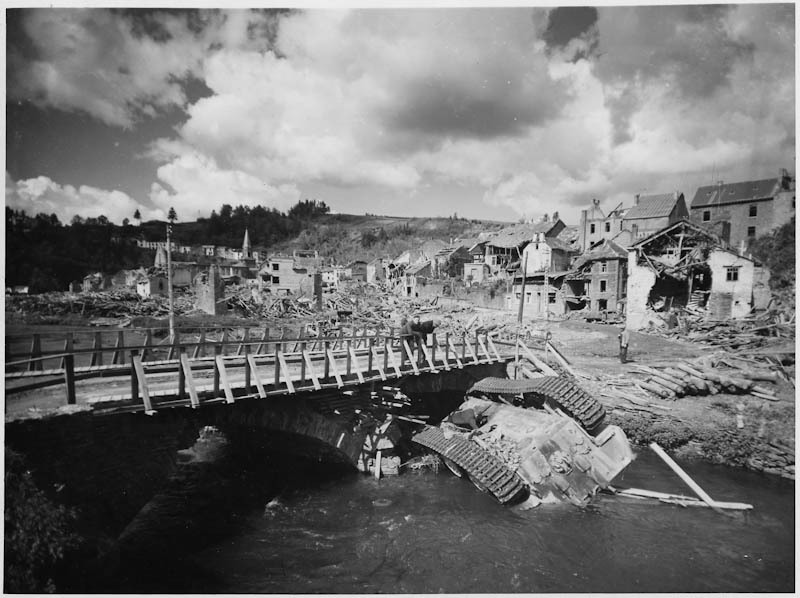
Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge was the last major German offensive. It was fought from December 16, 1944 - January 25, 1945.

War Bonds
The U.S. treasury used war bonds as a way to control inflation and raise money for the war.

Fireside Chats
During his presidency, FDR gave many Fireside Chats to the nation, including information on the progress of the war.

Industry
Industry in the U.S., which had been badly hurt by the Great Depression, was bolstered by wartime production

Japan
Japan was the leader of the Axis powers in the Pacific Theatre. It began fighting China in 1937.
 https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/map/pacific-basin-japanese-expansion
https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/map/pacific-basin-japanese-expansionFrance
France joined WWII on September 3, 1939 after the invasion of Poland.

D-Day
On D-Day, June 6, 1944, the Invasion of Normandy began, in which the Western Allied nations began to liberate mainland Europe from Nazi occupation.

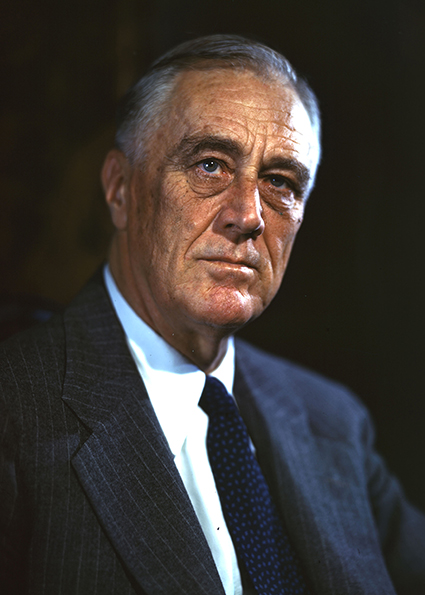
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt was the President of the United States from 1933-45. He passed away on April 12, 1945, just before the wars' end.
 http://www.fdrlibrary.marist.edu/archives/collections/franklin/index.php?p=digitallibrary/digitalcontent&id=4320
http://www.fdrlibrary.marist.edu/archives/collections/franklin/index.php?p=digitallibrary/digitalcontent&id=4320Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill served as Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1940-45.

Neville Chamberlain
Neville Chamberlain served as Prime Minister of Great Britatin from 1937-40.

Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek served as Generalissimo of the National Government of the Republic of China.

Charles de Gaulle
Charles de Gaulle led the Free French Forces from 1940-44.

Harry Truman
Harry S. Truman became President of the United States in 1945 after the passing of FDR.

Joseph Stalin
Joseph Stalin was the head of the Soviet Union during WWII.

Hirohito
Hirohito was Emperor of Japan during WWII.

Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini was the Prime Minister of Italy from 1922-43.

Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was the chancellor of Germany during WWII.

Iwo Jima
The Battle of Iwo Jima, February 19 - March 26, 1945, produced some of the fiercest fighting in the Pacific Campaign during WWII.

Battle of Midway
The Battle of Midway, June 4 - June 7, 1942, the United States was able to decisively defeat the Japanese Navy and gain the strategic advantage in the Pacific.

Blackouts
During blackouts, people had to cover their doors and windows with blackout curtains, cardboard or paint. This would prevent light from escaping and aiding enemy aircraft during bombings.

Scrap Drives
Along with rationing, there were also scrap drives which were campaigns to save and reuse vital materials.

Victory Gardens
A victory garden was a private garden planted during the war to help reduce pressure on the public food supply.

Hungary
Hungary joined WWII on June 22, 1941 after the invasion of the Soviet Union.

Australia
Australia joined WWII on September 3, 1939 after the invasion of Poland.

V-E Day
V-E Day, or Victory in Europe Day, was May 7 & 8, 1945.

V-J Day
V-J Day, or Victory over Japan Day, was August 15, 1945 & September 2, 1945.

Sudetenland
The Sudetenland was an area of Czechoslovakia that was annexed by Germany before the start of the war.

Lend-Lease & Destroyers for Bases
Lend-Lease & Destroyers for Bases were programs between the U.S. & other Allied nations to help war efforts of those countries before the U.S. formally entered the war.

The Big Three
The Big Three were Franklin D. Roosevelt, Winston Churchill & Joseph Stalin.

Kristallnacht
Kristallnacht, "the Night of Broken Glass," took place on November 9-10, 1938. On this night there were attacks on Jewish people and their property by the Nazis.

Mein Kampf
Mein Kampf, or My Battle, was a book dictated by Adolf Hitler.

Kamikaze
Kamikazes were Japanese suicide aviators intent on sinking Allied warships by flying their planes into them.

Home Front
The "Home Front" refers to efforts taken in the U.S. such as rationing and scrap drives to support the war effort.

Appeasement
Appeasement refers to the foreign policy of Chamberlain towards Nazi Germany from 1937-39.

European Theatre
The European Theatre was the area of heavy fighting during WWII.

Pacific Theatre
The Pacific Theatre was the area of military activity in the Pacific Ocean and the countries surrounding it during WWII. https://www.loc.gov/pictures/item/92520274/
https://www.loc.gov/pictures/item/92520274/Battle of Stalingrad
During the Battle of Stalingrad, July 17, 1942 - February 2, 1943, Germany and the Soviet Union battled for control of the city of Stalingrad.

Battle of Guadalcanal
The Battle of Guadalcanal, August 7, 1942 - February 9, 1943, was the first major offensive launched by the Allies against the Japanese.

Invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany on September 1, 1939 started WWII.

Women Airforce Service Pilots
WASPs were an organization of cilivian female pilots employed to fly military aircraft under the United States Army Air Forces.

Romania
Romania joined the Axis powers on November 23, 1940.

Canada
Canada joined WWII on September 10, 1939 after the invasion of Poland.

Concentration Camps
Concentration Camps were used heavily by the Nazis during WWII as a place for prisoners of the state.

Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a highly secret program to develop the atomic bomb.

Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement laid out the occupation of Germany and the reconstruction of Europe after the end of the war.
Tuskegee Airmen
The Tuskegee Airmen were a group of African-American pilots during WWII.

Internment Camps
During WWII, there were internment camps for Japanese-Americans in the U.S. These were established because many people feared that Japanese-Americans might be working as spies or saboteurs.

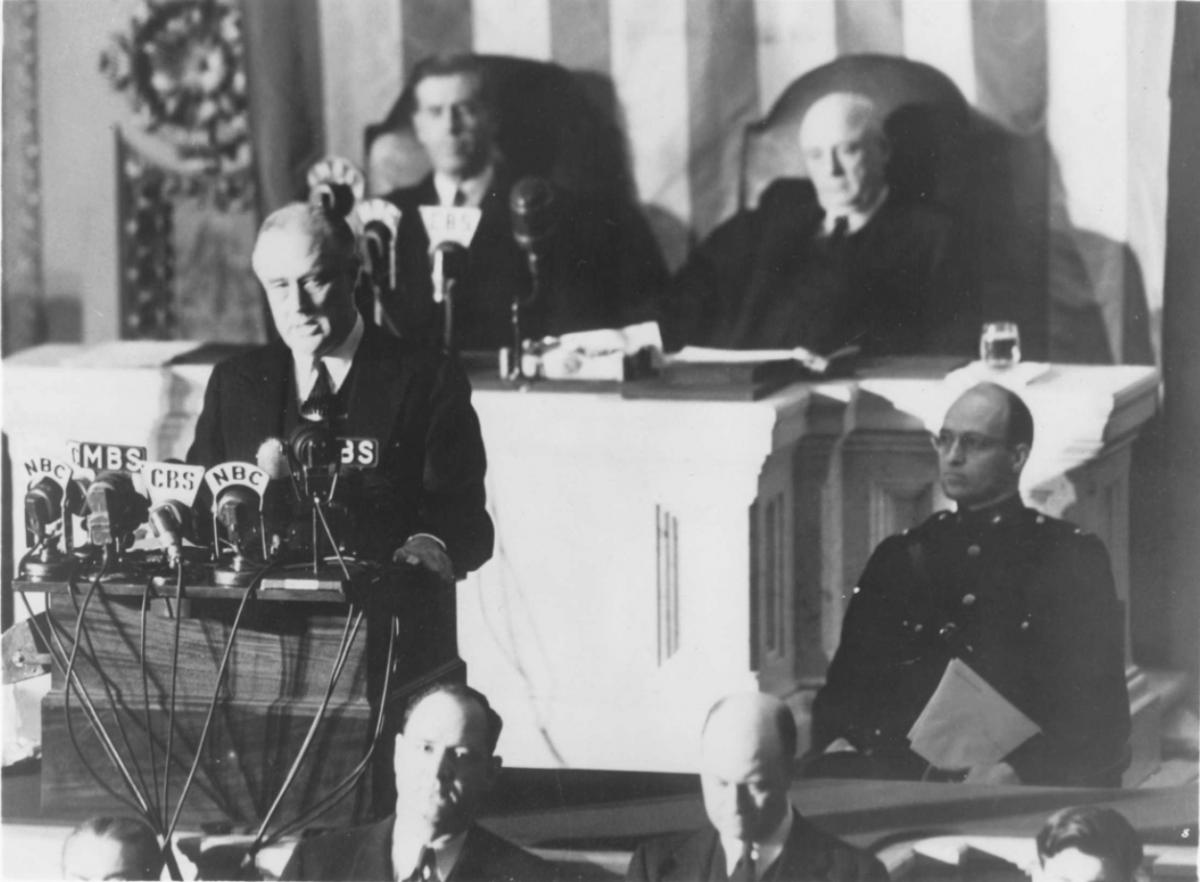
Day of Infamy Speech
The "Day of Infamy" speech was delivered before Congress on December 8, 1941, the day after the bombing of Pearl Harbor.

Munich Agreement
The Munich Agreement permitted Germany to annex the Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia.

Enola Gay
The Enola Gay was the plane that dropped the atomic bombs on Hiroshima.

Nazism
Nazism was the political movement in Germany under Hitler.

Gestapo
The Gestapo was the official secret police of Nazi Germany.

Fascism
Fascism was the political movement in Italy under Mussolini.

Blitzkrieg
The term "blitzkrieg", or lightning warfare, refers to a swift and sudden military offensive.

Pearl Harbor
On December 7, 1941, the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbor, which led to the U.S. entering the war.

Doolittle Raid
During the Doolittle Raid, April 18, 1942, the U.S. dropped bomb on Tokyo, Japan.

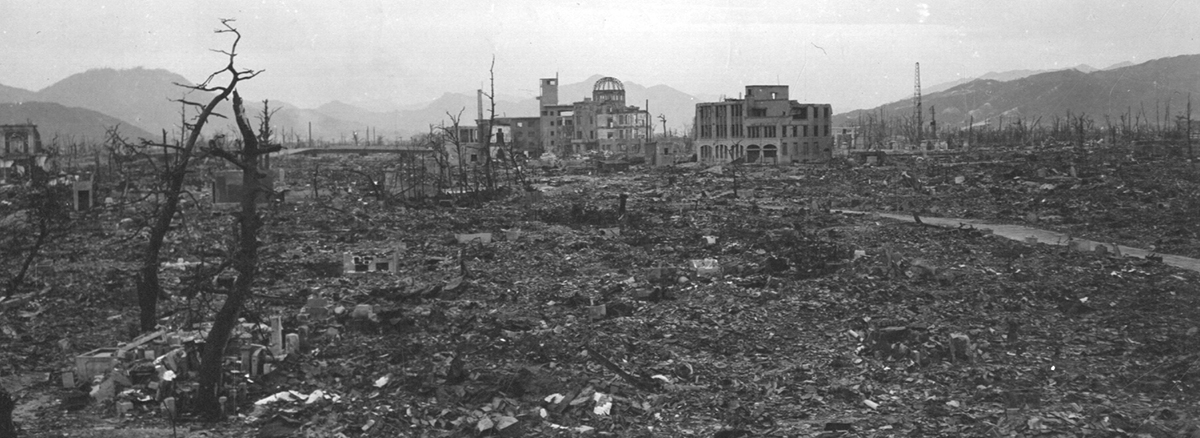
Hiroshima and Nagasaki
During August of 1945, the U.S. dropped two atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. These bombing led to the quick end of the war in Japan.

Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia was occupied by the Axis powers during WWII and in 1941, briefly became a member of the Axis powers.

Bulgaria
Bulgaria joined the Axis powers on March 1, 1941.

Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia's government-in-exile joined WWII on October 2, 1939.

Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the code name for the invasion of Northwest Europe by the Allied forces.

"Final Solution"
The "FInal Solution" was a plan by the Nazis to eliminate all of the European Jews.

Gas Chamber
Gas chambers were used by the Nazis in their concentration camps as a way to systemicatically kill Jews and other prisoners.

Schutzstaffel
The S.S., or Schutzstaffel, was the Nazis paramilitary force. The S.S. was responsible for many of the crimes against humanity committed by the Nazis.

Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact
The Nazi-Soviet Non-Aggression Pact, signed August 24, 1939, was a pledge of neutrality made by the Soviets and the Germans.

Nuremberg Trials
The Nuremberg Trials were trials against leaders of the Nazi party after the war.

Four Freedoms
FDR's Four Freedoms were found fundamental human freedoms. They were Freedom of Speech, Freedom of Religion, Freedom of Want, and Freedom of Fear.

"Germany First"
"Germany First" was the military strategy of the U.S. & U.K. during the war. It meant that the primary focus of the war was to be on Europe.

United Service Organizations
The USO, of United Servie Organization, provided a morale boost and recreational services for active military members.

United Nations
The United Nations, founded in 1945, was formed to prevent wars between countries and to provide a place for dialogue between nations.

Holocaust
The Holocaust was the genocide of the European Jews by the Nazis during WWII.
Atlantic Conference
The Atlantic Conference between Roosevelt and Churchill, took place aboard warships in Ship Harbour, Newfoundland. The result of this conference was the Atlantic Charter.

Casablanca Conference
The Casablanca Conference, between Roosevelt, Churchill, de Gaulle & Henri Giraud, created a declaration of “unconditional surrender” for the Axis powers.

Quebec Conference
The Quebec Conference, attended by Roosevelt, Churchill & William Mackenzie King, set D-Day for 1944.

Cairo Conference
The Cairo Conference, attended by Roosevelt, Churchill & Chiang Kai-shek, produced the Cairo Declaration for postwar Asia.

Teheran Conference
The Teheran Conference, attended by Roosevelt, Churchill & Stalin, was the first meeting of the Big Three.

Bretton Woods Conference
The Bretton Woods Conference established the International Monetary Fund & the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development.

Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference, attended by Roosevelt, Churchill and Stalin, established the final plans for the defeat of Germany as well as plans for postwar Europe.

Conference on International Organizations
The United Nations Conference of International Organization produced the United Nations Charter.

Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference, attended by Churchill, Stalin,Truman & Attlee, produced the Potsdam Declaration & the Potsdam Agreement.

George Marshall
George Marshall supervised the U.S. Army during WWII and was the chief military advisor to FDR.

Dwight D. Eisenhower
Dwight D. Eisenhower served as Supreme Commander of the Allied forces in Europe.

George S. Patton
George S. Patton was an Army General who commanded forces in North Africa, Sicily & the European Theatre.

Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur was the Supreme Commander of Allied forces in the Southwest Pacific Area.

James Doolittle
James Doolittle led the famous Doolittle Raid and bombing of Japan during WWII.

U-boats
U-boats were German submarines.

Higgins Boats
Higgins boats were landing craft used extensively during WWII.

Balloon Bomb
The balloon bomb was an experimental weapon used by Japan during WWII.

Bat Bomb
Bat bombs were small incendiary bombs attached to bats that were designed to start fires in the eaves and attics of buildings that the bats would roost in.

Atomic Bombs "Little Boy" & "Fat Man"
The atomic bombs "Little Boy" & "Fat Man" were bombs dropped on Hiroshima & Nagasaki by the U.S.

Flying Fortress
The Flying Fortress was a Boeing B-17 heavy bomber aircraft used extensively by the U.S. during WWII.

MAGIC Code
The MAGIC Code was the code name given to intercepted and decoded Japanese messages.
Enigma Machine
Enigma Machines were used for the encryption and decryption of secret coded messages.

Code Talkers
The code talkers were Navajo-speaking Native Americans used by the Marine Corps to transit secret messages.

Radar
Early warning radar networks were first introduced during WWII and greatly contributed to the Allied victory.

Chester Nimitz
Chester Nimitz was the Commander in Chief, Pacific Fleet for U.S. Naval forces & Commander in Chief, Pacific Ocean Areas for U.S. & Allied air, land and sea forces.

Adolf Eichmann
Adolf Eichmann was a Nazi who is considered to be the "architect of the Holocaust".

Erwin Rommel
Erwin Rommel was a German Field Marshal who commanded the German forces opposing the Allied forces during the Invasion of Normandy.

Isoroku Yamamoto
Isoroku Yamamoto was the commander-in-chief of the Japanese Combined Fleet during WWII.




